使用Django和Flask獲取訪問來源referrer
request.referrer # 來路request.headers.get(’User-Agent’) # 請求頭Django
request.META[’HTTP_REFERER’] # 來路request.META.get('HTTP_USER_AGENT') # 請求頭
補(bǔ)充:flask 重定向到上一個頁面,referrer、next參數(shù) --
>重定向會上一個頁面在某些場景下,我們需要在用戶訪問某個url后重定向會上一個頁面,比如用戶點(diǎn)擊某個需要登錄才能訪問的連接,這時程序會重定向到登錄頁面,當(dāng)用戶登錄后比較合理的行為是重定向到用戶登錄前瀏覽的頁面。
下面的例中,在foo和bar視圖中生成連接,鏈接過去后,沒有重定向會上一個頁面
@app.route(’/foo’)def foo():return ’<h1>Foo page </h1><a href='http://m.propowerdrill.cn/bcjs/%s' rel='external nofollow' rel='external nofollow' rel='external nofollow' rel='external nofollow' >Do something</a>’ %url_for(’do_something’)@app.route(’/bar’)def bar():return ’<h1>Bar page</h1><a href='http://m.propowerdrill.cn/bcjs/%s' rel='external nofollow' rel='external nofollow' rel='external nofollow' rel='external nofollow' >Do something </a>’ % url_for(’do_something’)@app.route(’/do_something’)def do_something():return redirect(url_for(’hello’))@app.route(’/hello’)def hello():name = request.args.get(’name’)if name is None:name = request.cookies.get(’name’,’xiaxiaoxu’)#從cookie中獲取name值response = ’<h1>Hello, %s</h1>’ % namereturn responseif __name__ == ’__main__’:app.run(debug = True)
結(jié)果:
訪問127.0.0.1:5000/foo或者127.0.0.1:5000/bar后,頁面出現(xiàn)連接,點(diǎn)擊鏈接后,進(jìn)入hello頁面,之后停留在了hello頁面
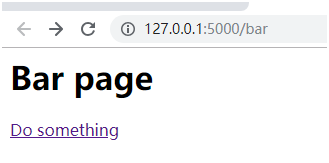
點(diǎn)擊鏈接后重定向到了hello頁面
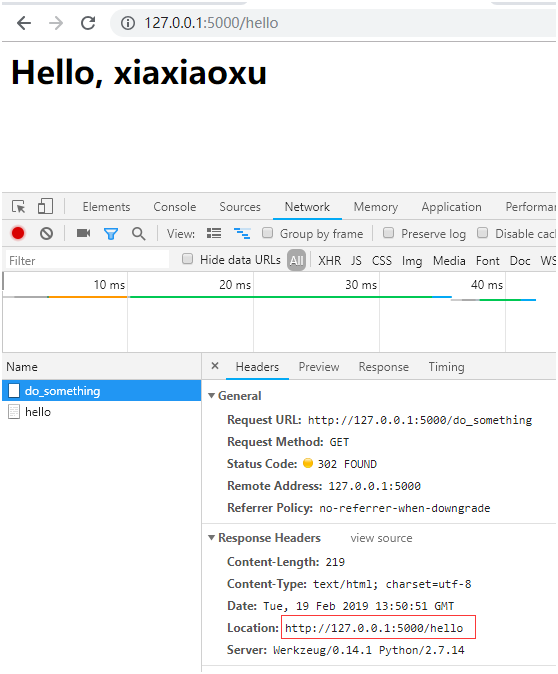
我們的目的是在鏈接后,返回原來的頁面
重定向會上一個頁面,關(guān)鍵是獲取上一個頁面的URL。
獲取上一個頁面的URL有兩種方法:HTTP referrerHTTP referrer是一個用來記錄請求發(fā)源地址的HTTP首部字段(HTTP_REFERER),即訪問來源。當(dāng)用戶在某個站點(diǎn)點(diǎn)擊鏈接,瀏覽器想新鏈接所在的服務(wù)器發(fā)起請求,請求的數(shù)據(jù)中包含的HTTP_REFERER字段記錄了用戶所在的原站點(diǎn)URL。
在flask中,referer的值可以通過請求對象的referrer屬性獲取,即request.referrer
修改do_something視圖函數(shù):
@app.route(’/do_something’)def do_something():return redirect(request.referrer)
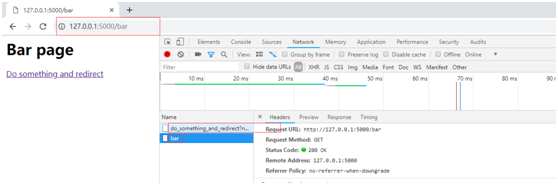
在bar頁面上再次點(diǎn)擊鏈接
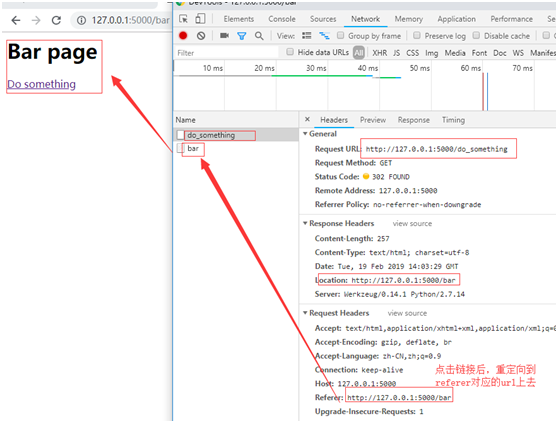
有的時候,referrer字段可能是空值,比如用戶直接在瀏覽器地址欄輸入URL或者因?yàn)榉阑饓蛘邽g覽器設(shè)置自動清除或修改referer字段,我們需要添加一個備選項(xiàng):
return redirect(request.referrer or url_for(’hello’))查詢參數(shù)next
除了自動從referrer獲取,另一種更常見的方式是在URL中手動加入包含當(dāng)前頁面URL的查詢參數(shù),這個查詢參數(shù)一般命名為next
在bar視圖中的鏈接do_something對應(yīng)的視圖添加next參數(shù)(在/do_someghing后加參數(shù))
def bar():#print dir(request)print 'request.full_path:',request.full_path#print 'request.url:',request.urlreturn ’<h1>Bar page</h1><a href='http://m.propowerdrill.cn/bcjs/%s' rel='external nofollow' rel='external nofollow' rel='external nofollow' rel='external nofollow' >Do something and redirect </a>’ % url_for(’do_something’, next = request.full_path)@app.route(’/do_something’)def do_something():return redirect(request.args.get(’next’))
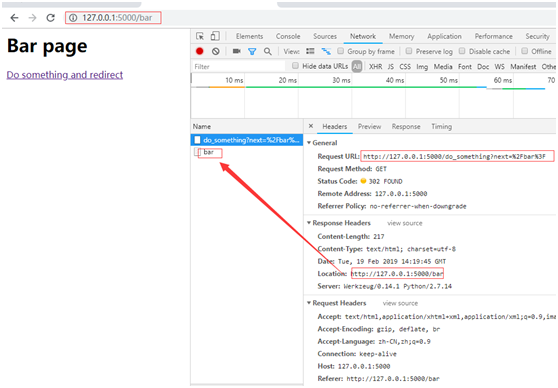
為了避免next參數(shù)為空的情況,也可以加備選項(xiàng),如果為空就重定向到hello視圖
return redirect(request.args.get(’next’, url_for(’hello’)))為了覆蓋更全面,可以將查詢參數(shù)next和referrer兩種方式結(jié)合起來使用:
先獲取next參數(shù),如果為空就嘗試獲取referer,如果仍然為空,就重定向到默認(rèn)的hello視圖
因?yàn)樵诓煌晥D執(zhí)行這部分操作的代碼相同,我們可以創(chuàng)建一個通用的函數(shù)redirect_back()函數(shù)
在do_something視圖中調(diào)用這個函數(shù)
@app.route(’/bar’)def bar():print 'request.full_path:',request.full_pathreturn ’<h1>Bar page</h1><a href='http://m.propowerdrill.cn/bcjs/%s' rel='external nofollow' rel='external nofollow' rel='external nofollow' rel='external nofollow' >Do something and redirect </a>’ % url_for(’do_something’, next = request.full_path)def redirect_back(default = ’hello’,**kwargs):for target in request.args.get(’next’),request.referrer:if target:return redirect(target)return redirect(url_for(default,**kwargs))@app.route(’/do_something_and_redirect’)def do_something():return redirect_back()if __name__ == ’__main__’:app.run(debug = True)
以上為個人經(jīng)驗(yàn),希望能給大家一個參考,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)。如有錯誤或未考慮完全的地方,望不吝賜教。
相關(guān)文章:
1. Java Bean 映射工具 Dozer 2.0 發(fā)布2. php字符串函數(shù) str類常見用法示例3. Springboot 跨域配置無效及接口訪問報錯的解決方法4. 用js編寫留言板5. Android實(shí)現(xiàn)下載進(jìn)度條效果6. WebSocket使用以及在vue如何使用問題7. python matplotlib模塊基本圖形繪制方法小結(jié)【直線,曲線,直方圖,餅圖等】8. PHP設(shè)計(jì)模式之迭代器模式淺析9. Spring框架配置java web實(shí)現(xiàn)實(shí)例化10. python argparse模塊通過后臺傳遞參數(shù)實(shí)例
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備